In the fertilizer industry, the most common type of cooler is the rotary drum cooler. It can be widely utilized to cool various materials, not only in organic fertilizer plants but compound fertilizer plants. In chemical fertilizer manufacturing, rotary cooling is necessary to decrease the temperature to prevent caking. In organic fertilizer production, the process is however to lower the temperature for easy distribution and packaging. The rotary cooler is simple to be operated with different models, and the dimension varies with its capacity, taking model LQJ-1.0 for example, the production capacity of LQJ-1.0 rotary drum cooler is 2-3 tons per hour with a size of 1080cm(L) x 221cm(W) x 170cm(H), mainly installed in small scale organic fertilizer plants.
Other benefits of rotary cooler/rotary cooling technology can be concluded:
★ continuous operation permits mass production;
★ ensures sufficient cooling with economic construction costs;
★ simply operating design but greatly increase the cooling speed;
★ plant layout convenience;
★ organic/bio fertilizer granules are cooled to remove the heat to prevent damage to bags and bagging equipment;
★ by rotary cooling, fertilizers decrease sharply at temperatures below 40℃, which greatly improves the quality and grindability of the granules.
The rotary cooler is considered to be an absolutely necessary part to make trustworthy compound & organic fertilizers in large system production line configuration.
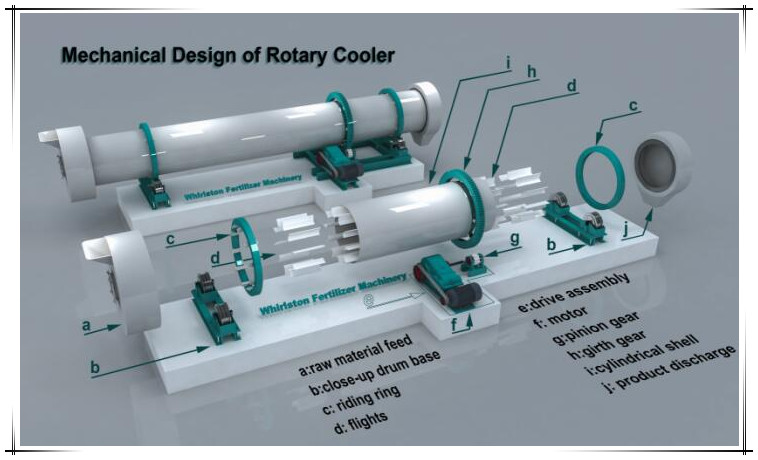
Generally speaking, rotary coolers consist of an organic fertilizer feeding end, riding ring, flights, motor, pinion gear, girth gear, cylindrical shell, discharge end, etc.
★ feeding end: after drying by the rotary dryer, organic fertilizer granules are transferred into the cooler machine by belt conveyor through the feed hopper at the higher end. Meanwhile, under the suction of the draught fan at the feed end, the airflow inside the cylinder speeds up.
★ riding ring: Cylindrical shell of the cooler is supported by two riding rings running on a set of rollers. The cooler equipment rotates on two forged steel races which are called riding rings. They add structural support for the rotary cylinder and serve as a place for pressure to be absorbed.
★ flights: it is also called “lifters”, affixed to the interior of the rotary drum. Flights are used in rotary dryers and rotary coolers to spread the material across the airflow in a uniform shower or curtain or to shower material through the process gas stream. They promote gas-solid contact. Lifting flights come in many sizes and shapes which can be individually tailored to the requirements of each cooler and product to achieve the best results.
★ pinion gear and girth gear: drive assembly of the rotary cooler consists of the main motor, gear reducer, girth gear, and pinion gear. a single girth gear pinion drive is used to drive the large, rotating cooling system. The gear wheel is connected to an electric motor with variable speed via a gear train. the main motor drives the belt and belt pulley and transfers to the driving shaft through the reducer. The pinion which is installed on the driving shaft engages with the gear fixed on the machine body, working in the opposite direction to make the cylinder rotate.
★ cylindrical shell: rotary coolers are made of a long cylindrical shell that is rotated around the longitudinal axis. The shell is usually slightly inclined horizontally to induce the flow of solids from one end of the cooler to the other.
★ the cooled materials flow out from the lower end of the rotary drum and are sent to the rotary screener by the belt conveyor. The tail gas enters the dust-settling chamber.
Combined Processes:
Drying
Granulating
Parameter of Organic Fertilizer Rotary Cooler:
| Name | Model | Dimension(CM) | Capacity (t/h) | Power (Kw) |
| L*W*H | ||||
| Rotary Cooler | LQJ-0.8 | 880x210x150 | 1-2 | 5.5 |
| LQJ-1.0 | 1080x221x170 | 2-3 | 7.5 | |
| LQJ-1.2 | 1300x236x180 | 3-5 | 7.5 | |
| LQJ-1.5 | 1630x280x226 | 6-10 | 11 | |
| LQJ-1.8 | 1950x330x245 | 8-14 | 22 |






